
The Role of Psychology in Healing Trauma
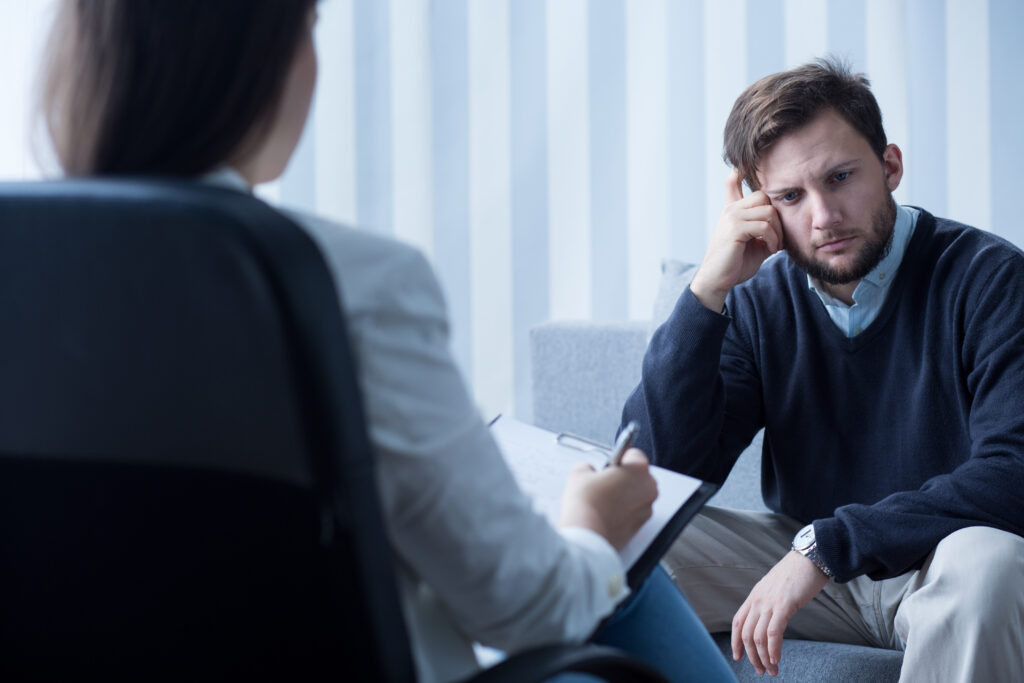
Trauma, a deeply distressing or disturbing experience, can leave lasting emotional and psychological scars. Healing from trauma is a complex process that often requires professional intervention, and psychology plays a crucial role in facilitating recovery. Understanding the role of psychology in healing trauma helps individuals and communities navigate the path toward resilience and well-being.
Understanding Trauma
Trauma can result from various events such as accidents, natural disasters, abuse, violence, or the sudden loss of a loved one. The impact of trauma varies widely, affecting individuals differently based on their experiences, support systems, and coping mechanisms. Psychological trauma disrupts an individual’s sense of safety, leading to symptoms such as anxiety, depression, flashbacks, and emotional numbness.
Psychology’s Role in Healing
- Assessment and Diagnosis
Psychologists use clinical assessments to understand the nature and severity of trauma. Accurate diagnosis is essential to tailoring effective treatment plans that address the individual’s specific symptoms and challenges. - Therapeutic Interventions
Several evidence-based psychological therapies are effective in treating trauma:
- Cognitive Behavioural Therapy (CBT): Helps individuals identify and change negative thought patterns related to the trauma.
- Eye Movement Desensitisation and Reprocessing (EMDR): Facilitates processing traumatic memories to reduce their emotional impact.
- Trauma-Focused Cognitive Behavioural Therapy (TF-CBT): Specifically designed for children and adolescents to address trauma.
- Psychodynamic Therapy: Explores unconscious processes and past experiences to understand trauma’s effects.
- Emotional Support and Validation
Psychology provides a safe space for individuals to express their feelings and fears. Therapists offer empathy, validation, and support, vital for rebuilding trust and self-esteem. - Developing Coping Strategies
Psychologists teach coping mechanisms to manage symptoms such as anxiety, panic attacks, and flashbacks. Techniques may include mindfulness, relaxation exercises, and stress management skills. - Promoting Resilience and Growth
Beyond symptom relief, psychology helps individuals find meaning in their experiences and develop resilience. Post-traumatic growth can lead to improved relationships, personal strength, and a renewed appreciation for life.
The Importance of Early Intervention
Timely psychological intervention can prevent the worsening of trauma symptoms and reduce the risk of developing chronic mental health disorders. Early support also encourages healthier coping strategies and faster recovery.
Conclusion
Psychology plays an indispensable role in healing trauma by providing assessment, therapeutic interventions, emotional support, and tools for resilience. Through professional psychological care, individuals affected by trauma can reclaim their lives, foster healing, and move toward a future marked by hope and recovery.
Leave a Reply